Organic solvents are widely used in industrial production, such as in rubber, adhesive tape, plastic, textile, printing, paint, military industry and other fields.
Organic solvents are mainly used to dissolve certain substances in the production of products, but they need to be removed after the product is formed, so a large amount of organic waste gas is generated.
The large-scale and uncontrolled emission of organic waste gas increases production costs, pollutes the environment and causes accidents.
Therefore, recycling and utilizing organic waste gas can not only ensure safe production and purify the environment, but also reduce production costs. It is an important part of chemical production.
1.Exhaust sources of solvent gases
In the petrochemical industry, printing industry, synthetic resin industry, rubber industry, etc., a relatively limited number of solvents are often used.
Those cited below are typical solvents utilized in various industrial sectors that can be recovered from activated carbon.
Film and flake production: ether, acetone, butanone, alcohol, tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane;
Printing industry: toluene, benzene, trichloroethylene, hexane;
Metal degreasing: trichloroethylene, trihelium ethane, perchloroethylene;
Rubber industry: gasoline, benzene, toluene;
Rayon and viscose yarn production: carbon disulfide;
Purification of chemical reagents: perchloroethylene, fluorinated hydrocarbons
Production of artificial leather and synthetic fibers: alcohol, ketone, hexane, toluene, ether, formyl dimethylamine
Production of glues and adhesives: gasoline, hexane, toluene.
In addition, the use of solvents is also involved in many industrial processes, but due to the relatively little research, it is not elaborated in this book.
2.Solvent recovery with activated carbon adsorption
Activated carbon has a large number of fine pores. It has a large specific surface area. It has a large adsorption capacity for exhaust gases, but a small adsorption capacity for water.
Therefore, activated carbon is most suitable for organic waste gas purification, and when its adsorption reaches saturation, it can be regenerated with water vapor to recover useful components.
Activated carbon adsorption is effective for low concentrations of solvents and for almost all solvents. Especially in the activated carbon adsorption method for low concentration solvents, it can be purified to the mg/kg level relatively easily.
This tendency shows the superiority of the activated carbon adsorption method in recycling for the purpose of combating public hazards.
1.Principle of solvent recovery with activated carbon
Solvent recovery aims to recycle organic waste gas through a certain recycling process and reuse it in production, thereby reducing air pollution and production costs.
The activated carbon adsorption method is used for solvent recovery, which is to use the excellent adsorption properties of activated carbon to adsorb and remove organic vapor and purify the air by passing organic solvent vapor into the activated carbon adsorption tower.
The activated carbon saturated with adsorption can be regenerated by water vapor, and the regenerated activated carbon can be recycled.
learn more:
Maximizing Cost Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Activated Carbon Regeneration Methods
The technology of activated carbon solvent recovery is suitable for gas recovery of solvents with a solvent vapor concentration of 1~20g/cm, and its recovery efficiency is greater than 90%;
The concentration of solvent vapor and air mixture can be kept below the lower explosion limit, so the production is relatively safe; the solvent recovery with activated carbon has low cost, simple process and a wide range of application.
2.Quality requirements of activated carbon for solvent recovery technology
Activated carbon is used for solvent adsorption recovery and needs to be recycled, so it is required to have good chemical stability, abrasion resistance, adsorption capacity and small bed resistance.
At present, activated carbon for solvent recovery has been produced in large quantities in China, among which the production of activated carbon for coal-based solvent recovery is mainly concentrated in the Ningxia Region and the surrounding areas in the northwest of China, with an annual production capacity of more than 80,000 tons, and the main quality indexes of the products are shown in Table 2-1.
| Table2-1 Main quality indexes of activated carbon for coal-based solvent recovery | |
| Diameter/mm | 1.5~5 |
| Stack density/(g/L) | 380~520 |
| Ash/% | 4~14 |
| Adsorption for CCl4/% | 60~90 |
| Iodine/(mg/g) | 900~1050 |
In addition to coal-based activated carbon for solvent recovery, the properties of various commonly used activated carbons for solvent recovery are shown in Table 2-2.
Table2-2 Properties of various activated carbons commonly used for solvent recovery
| Project | Pelletized activated carbon | Granular activated carbon | Powdered activated carbon | Fibrous activated carbon | Spherical activated carbon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw materials for manufacturing | Coal, , Wood, Nutshell, Nutlet | Coal, Wood | Coal, Wood, Nutshell, Nutlet | Synthetic fiber, Petroleum Systems, Coal Pitch, etc. | Coal, Petroleum System |
| True Density /(g/mL) | 2.0~2.2 | 0.9~2.2 | 2.0~2.2 | 1.9~2.1 | |
| Filling Destiny/(g/mL) | 0.35~0.60 | 0.35~0.60 | 0.15~0.60 | 0.03~0.10 | 0.50~0.65 |
| Bed voidage/ % | 33~45 | 33~45 | 45~75 | 90~98 | 33~42 |
| Pore volume /(cm3/g) | 0.5~1.1 | 0.5~1.2 | 0.4~1.0 | ||
| Surface area /(m2/g) | 700~1500 | 700~1500 | 700~1600 | 1000 | 800~1200 |
| Average pore size/nm | 1.2~3.0 | 1. 5~3. 0 | 1.5~3.0 | 0.3~4.5 | 1.5~2.5 |
| Thermal conductivity/[kJ/(m • h • K)] | 0.42~0.84 | ||||
| Specific heat capacity/[kJ/(kg • K)] | 0.84~1.05 |
3.Operation process of activated carbon solvent recovery device
The process of activated carbon solvent recovery mainly consists of the following 4 basic stages.
1.Adsorption: The adsorption process can continue from the activated carbon layer to the outlet of the adsorption zone, so that it reaches the limit of the venting concentration.
2.Desorption: The adsorption saturated activated carbon is regenerated by water vapor at 120~140℃; for high boiling point solvents, it is necessary to increase the vapor’s temperature.
For desorption, an extractive elution portion of the solvent can be used until the final temperature of the carbon layer. For solvents that decompose easily, the desorption process requires caution.
Some require additional heating device in the activated carbon layer, which reduces the amount of vapor used and increases the concentration of condensate. The steam used is partly for desorption and partly for elution.
For wet activated carbon, the amount used for desorption and elution will be different because a lot of energy is required to desorb the water adsorbed by the activated carbon.
In most cases, vapor desorption for 30~40 minutes is sufficient, but 60 minutes is rarely seen. In part, this is related to the humidity of the vapor used.
3.Desiccation: At the end of the desorption process by vapor displacement, the pores of the activated carbon and the gaps between the carbon particles are saturated with water vapor.
This greatly reduces the adsorption of large quantities of solvents in the secondary cycle. Therefore, the carbon layer should be dry, which is usually accomplished with hot air and dry vapor.
4.Cooling: After drying, the activated carbon layer is cooled down to at least 40°C. The contact of the solvent with the hot carbon can lead to an exothermic reaction of cracking or oxidation.
In the limit, these exothermic reactions can cause local overheating and spontaneous combustion of the carbon layer. The relationship between the consumption of cold air and the structure of the adsorber is that 1t of activated carbon requires 50~200m³ of cold air.
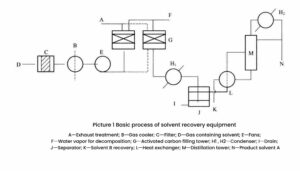
Adsorption operating conditions: Since the operating conditions of the activated carbon filling layer vary depending on the type of activated carbon, especially the specific surface area of the adsorption pores, pore size distribution, filling layer height, filling method, original gas conditions, etc., it cannot be discussed according to a single condition.
However, as an example, the operating conditions for an efficiency of 98% are shown in Table 2.
| Table 2 Example of operating conditions for activated carbon adsorption device | ||
|---|---|---|
| Activated carbon used | Layer height of activated carbon/mm | 300~700 |
| Particle size/mesh | 4~6 | |
| Fill density/(kg/m3) | 380~420 | |
| BET Specific surface area/(m2/g) | 1100~1500 | |
| Aperture(50%)/nm | 1.8~2.2 | |
| Benzene adsorption rate/(g/g) | 0.30~0.35 | |
| Adsorption conditions | Airflow direction | Upward flow |
| Linear velocity of gas/(m/s) | 0. 40~0. 55 | |
| Gas temperature at the inlet of the adsorption tower /℃ | 30~50 | |
| Gas humidity at the inlet of the adsorption tower /(relative humidity)/% | roughly40 | |
| Adsorption load/(g/g) | roughly0.20 | |
Here, the linear velocity of the gas is an important factor that makes it possible to miniaturize the adsorption device, as well as for processes such as drying.
However, with the increase of linear velocity, there will be an unsuitable situation due to the increase of pressure loss, the local movement of the activated carbon particles themselves, or the vortex phenomenon, so there is a certain upper limit.
3.Application of activated carbon solvent recovery technology
Activated carbon solvent recovery technology has been successfully applied in many industries such as printing, paint, rubber, tape, explosives, film, asbestos products, papermaking and synthetic fibers. And it has achieved significant social and environmental benefits.
For example, after adopting activated carbon recovery technology, a paper mill reduced solvent consumption by about 60% and gained an annual net profit of about 700,000 yuan, while the surrounding atmospheric environment was significantly improved;
After a pencil factory, a piano factory and other units adopted the newly developed activated carbon solvent recovery technology, the quality of the atmosphere in the working environment was significantly improved, and the content of benzene, toluene and other hazardous substances in the atmosphere was reduced from several hundred milligrams per cubic meter to several dozen milligrams per cubic meter, with a purification efficiency of 90%;
According to information, a chemical fiber factory uses activated carbon solvent recovery technology to recover carbon disulfide with a recovery rate of nearly 90%, which reduces air pollution, significantly improves the working environment, and reduces production costs.
At present, many industries in my country have adopted activated carbon solvent recovery technology and recover more than a dozen solvents, effectively reducing air pollution and reducing production costs. The industries in my country that use activated carbon solvent recovery and the recovered solvents are detailed in Table 3.
|
Table 3 Application scope of activated carbon solvent recovery technology |
|
| Application scope | Recovered solvents |
| Explosive production | Ethanol, ether, acetone |
| Printing and ink | Xylene, toluene, benzene, ethanol, crude gasoline |
| Dry cleaning, metal degreasing | Gasoline, benzene, tetrafluoroethylene |
| Synthetic fiber production | Ether, ethanol, acetone, carbon disulfide |
| Rubber industry | Petrol, benzene, toluene |
| Celluloid | Ethanol |
| Film production | Ether, ethanol, acetone, dichloromethane |
| Paint production | Benzene, toluene, xylene |
| Foil production | Ether, ethanol, acetone, dichloromethane |
With the development of science and technology and the advancement of global industrialization, the use of solvents in various industries is becoming more and more widespread.
For example, synthetic resins, synthetic fibers, and the printing industry use a large number of aromatic solvents as well as alcohol and ester solvents, chlorocarbon solvents used in precision instrument manufacturing, and dichloromethane used in photographic film manufacturing.
The use of these solvents brings beneficial effects to industrialized production as well as environmental problems. Therefore, the prevention of solvent evaporation, recovery and harmless disposal of solvents will be necessary and essential from the perspective of environmental protection and energy conservation.
4.solvent recovery case for adhesive tape factory customer
It’s mainly used for tape factory adsorption of toluene, ethyl acetate


Demand Specifications:
CTC Adsorption: Min. 80 %
Total Ash Content: Max. 10 %
Ball Pan Hardness: Min. 95 %
Moisture Content:as packed Max. 5%
Bulk Density: Min 360 kg/m3
Pellet Diameter Tolerance:3.6 – 4.4 mm
General Characteristics
Surface Area: 1250 m2 / kg
Tapped Density: 350 – 400 kg/m3
Filling Density: 300 – 340 kg/m3
Pellet Diameter Tolerance: ±5%
On the basis of CTC of 80%, the customer required a large specific surface area. At the same time, the customer’s previous activated carbon had a phenomenon of chalking after multiple desorption in one and a half years, so our fully automatic visual batching system is needed to operate to meet the customer’s requirements of specific surface area and strength. The strength of our columnar activated carbon has been tested to be more than 98%.
this is our pelletized AC quality control video:
learn more:






