Heycarbons Catalytic Activated Carbon Manufacturer From China
- Over 20 years of experience in catalytic activated carbon manufacturing.
- The annual output of activated carbon is 18,000 tons.
- 16pcs Production Patents.
- Catalysts include various metal oxides, noble metal ions
You will get a quote in 24 hours

Main Applications:
- Phosgene production and destruction
- Cyanuric chloride production
- Sulfuryl chloride production
- Flue gas SO2 conversion into H2SO4 for re-use, Reduction of Hydrogen Sulfide
- NOx removal from air,H2S removal from Biogas, VOCs removal
- Destruction of chloramine and bromate and hydrogen sulfide H2S from drinking water
- Reduction/Removal of Bad Tastes and Odours
- Special Carbon Filters
Heycarbons Catalytic Activated Carbon
Heycarbons is a leading catalytic activated carbon manufacture from China.
Activated carbon itself can be used as a catalyst in various isomerization, polymerization, oxidation and halogenation reactions. On the other hand, it is more important to use it as a catalyst carrier to load various catalysts.
Catalytic Activated Carbon (CAC) is an advanced form of traditional activated carbon, chemically or physically treated to develop a catalytically active surface, allowing it to accelerate specific chemical reactions.
Unlike regular activated carbon, CAC not only provides superior adsorption capabilities but also actively breaks down, converts, or removes various hazardous gases and pollutants.
Owing to these advantages, CAC is widely utilized in residential and commercial water filtration systems, industrial gas treatment for toxic emissions (like H₂S and SO₂), gas masks, liquid deodorization and decolorization, and in the food and beverage industry for impurity removal.
Catalytic activated carbon can also be combined with gac granular activated carbon for water purification filters to remove chloramines and hydrogen sulfide H2S .
Metal catalysts (e.g. Au, Pt, Pd, Ir, Ru, Rh, Ni, Co, Cu, Mg, Zn, Fe,Mn, V, etc.)
The following table shows the various catalyst types that can be loaded when activated carbon is used as a catalyst carrier. It can also load multiple catalysts.
You will get a quote in 24 hours
Heycarbons Catalytic Activated Carbon Types
| Catalyst type | Main Function | Main removal substances | Main application industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manganese dioxide (MnO₂) | 1. Catalyst: Promote oxidation reaction to remove heavy metals: Adsorb lead, arsenic, etc. 2. Oxidant: Degrade organic pollutants 3. Improve adsorption performance: Enhance the removal of pollutants 4. Remove chlorine: Improve water quality | 1. Heavy metals: lead (Pb), arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd) 2. Organic pollutants: ammonia nitrogen (NH₃), benzene series (such as benzene C₆H₆) 3. Residual chlorine: chlorine (Cl₂) 4. Manganese: manganese (Mn) | Water treatment plants, environmental protection companies, chemical plants, mining companies, food and beverage plants, pharmaceutical plants, power companies |
| Iron oxide (Fe₂O₃) | 1. Enhanced adsorption: Improve the adsorption efficiency of heavy metals and organic matter 2. Catalytic reaction: Promote oxidation reaction and increase degradation rate 3. Redox: Participate in pollutant removal reaction 4. Improved stability: Enhanced durability and environmental adaptability | 1. Heavy metals: lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd) 2. Organic pollutants: organic compounds (VOCs), ammonia nitrogen (NH₃), benzene series (such as benzene C₆H₆) 3. Color substances: dyes, such as methylene blue (C₁₆H₁₈N₃S) 4. Odor substances: hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) | Water treatment plants, chemical plants, pharmaceutical plants, food processing plants, paper mills, power plants |
| Copper Oxide (CuO) | 1. Catalyst: used in organic synthesis and waste gas treatment 2. Oxidation of organic pollutants: degradation of difficult-to-treat pollutants 3. Increase reaction rate: accelerate the treatment process 4. Anticorrosion and antibacterial effects: enhance the durability and safety of materials | 1. Organic pollutants: benzene (C₆H₆), alcohols (ethanol C₂H₅OH) 2. Nitrogen oxides: nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) 3. Sulfides: hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) 4. Heavy metals: lead (Pb),copper (Cu) 5. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): toluene (C₇H₈),xylene (C₈H₁₀) | Water treatment plants, waste gas treatment plants, chemical plants, food processing plants, pharmaceutical plants, power plants |
| Magnesium oxide (MgO) | 1. Enhance adsorption performance: improve the adsorption of heavy metals and organic pollutants 2. Catalysis: promote certain chemical reactions and improve pollutant removal efficiency 3. Improve pore structure: improve the pore structure of activated carbon and increase specific surface area 4. Improve thermal stability: enhance performance stability under high temperature environment 5. Water treatment application: remove pollutants such as ammonia nitrogen and phosphate in water | 1. Heavy metals: such as lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg) 2. Ammonia nitrogen: NH₄ 3. Phosphate: PO₄ 4. Organic pollutants: such as benzene (C₆H₆), phenol (C₆H₅OH), etc. 5. Sulfides: such as hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) | Water treatment plants, chemical plants, electroplating plants, pharmaceutical plants |
| Cobalt oxide (Co₃O₄) | 1. Catalytic decomposition of pollutants, used for wastewater treatment 2. Enhance oxidation capacity, more effectively degrade harmful substances 3. Improve electrochemical performance, suitable for capacitors and other equipment 4. Purify toxic gases, used for air purification | 1. Organic pollutants: such as phenol (C₆H₅OH), formaldehyde (HCHO), ammonia (NH₃) 2. Toxic gases: carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ, including NO and NO₂) 3. Heavy metals: such as lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd) | Chemical plants, pharmaceutical plants, electronics manufacturing plants, metallurgical plants, electroplating plants |
| Vanadium (V) | 1. Improve oxidation capacity: used to remove pollutants such as SO₂ and NOₓ 2. Improve selectivity: more effective in decomposing specific organic matter (such as VOC) 3. Assist water treatment: help degrade organic pollutants in wastewater 4. Increase stability: improve the antioxidant properties of activated carbon | 1. Sulfur dioxide (SO₂): 2. Nitrogen oxides: Nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) 3. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs):toluene (C₇H₈), benzene (C₆H₆),xylene (C₈H₁₀) 4. Organic pollutants: Phenol (C₆H₅OH) | Waste gas treatment plants, chemical plants, water treatment plants, pharmaceutical plants, oil refineries |
| Nickel (Ni) | 1. Catalyst: used to promote chemical reactions such as hydrogenation and organic synthesis 2. Enhanced adsorption: improve the adsorption capacity of activated carbon for specific substances 3. Improved selectivity: adjust the nickel loading to optimize the selectivity of the reaction 4. Wastewater treatment: remove heavy metals and organic pollutants from water 5. Electrocatalysis: used in batteries and fuel cells to improve energy conversion efficiency | 1. Organic pollutants: benzene (C₆H₆) and its derivatives, ethanol, C₂H₅OH) 2. Heavy metals: nickel (Ni) lead (Pb) mercury (Hg) copper (Cu) 3. Nitrogen compounds: ammonia (NH₃) nitrate (NO₃⁻) 4. Dye: methylene blue (C₁₆H₁₈N₃S) | Chemical plants, sewage treatment plants, battery manufacturers, food processing plants, pharmaceutical plants, environmental management companies |
| Platinum (Pt) | 1. Catalyst: used to reduce harmful gases emitted by automobiles 2. Environmental governance: improve the degradation efficiency of organic pollutants 3. Electrocatalysis: improve the reaction efficiency of fuel cells 4. Drug release: enhance the release control of drugs 5. Gas adsorption: improve gas adsorption and separation | 1. Organic pollutants: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), benzene (C₆H₆), formaldehyde (CH₂O) 2. Nitrogen oxides: Nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) 3. Sulfides: Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) 4. Heavy metals: Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd) 5. Hydrogen: Hydrogen (H₂) | Petrochemical plants, automobile manufacturing plants, pharmaceutical plants, electronics and semiconductor plants, battery and fuel cell plants |
| Palladium (Pd) | 1. Hydrogenation reaction: accelerate the hydrogenation of organic matter 2. Removal of impurities: remove pollutants in water 3. Dechlorination treatment: treat harmful organic chlorides 4. Oxidation reaction: purify air and exhaust gas | 1. Chloride: Chlorine (Cl₂), Hydrogen chloride (HCl) 2. Nitrate: Nitrate (NO₃⁻) 3. Organic chloride: Chloroform (CHCl₃), Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) 4. Carbon monoxide: CO | Chemical plants, pharmaceutical plants, water treatment plants, environmental protection plants |
| Silver (Ag) | 1. Antibacterial disinfection: kill bacteria and viruses, purify water and air 2. Remove odor: absorb odor and prevent microbial growth 3. Extend life: antibacterial effect delays activated carbon aging | 1. Bacteria and viruses: common microbial contaminants 2. Chloride: Chlorine (Cl₂) 3. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Formaldehyde (CH₂O), Benzene (C₆H₆), Toluene (C₇H₈) 4. Odor: Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) | Water treatment plants, food and beverage industries, pharmaceutical plants, chemical plants, air purification equipment manufacturers, hospitals and medical equipment manufacturers |
| Potassium carbonate (K2CO3) | 1. Improve adsorption capacity: Enhance adsorption of pollutants 2. Catalytic reaction: Promote chemical reaction efficiency 3. Selective adsorption: Enhance adsorption of specific ions, suitable for water treatment 4. Improve pore structure: Improve adsorption performance 5. Remove gas: Effectively remove carbon dioxide and ammonia | 1. Carbon dioxide: CO₂ 2. Ammonia: NH₃ 3. Hydrogen sulfide: H₂S 4. Heavy metals: lead (Pb) copper (Cu) | Power plants, steel plants,paper mills… Water treatment plants, sewage treatment plants, chemical plants, metallurgical plants, environmental protection equipment manufacturing plants |
| Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) | 1. Improve adsorption capacity: enhance the adsorption of organic matter and metal ions 2. Promote reaction: improve removal efficiency 3. Adjust pH value: optimize pH and improve adsorption 4. Improve regeneration capacity: improve regeneration performance and reduce costs 5. Enhance stability: improve stability under extreme conditions | 1. Organic matter: benzene (C₆H₆), phenol (C₆H₅OH), ethanol (C₂H₅OH) 2. Heavy metals: lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg) 3. Acidic gases: sulfur dioxide (SO₂), ammonia (NH₃) 4. Fluoride: such as hydrogen fluoride (HF) 5. Pigment: methacrylic acid (C₁₄H₁₈N₂O₄S) | Mainly concentrated in industries that need to deal with acidic gases and harmful pollutants. Steel mills, oil refineries, chemical plants, pharmaceutical plants, food processing plants, electronic manufacturing plants, paper mills, waste incineration plants, power plants, metal smelters |
| Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) | 1. Enhance adsorption capacity: better removal of acidic gases and heavy metals 2. Neutralize acidity: suitable for waste gas and wastewater treatment 3. Reduce costs: save materials 4. Increase strength: more durable | 1. Sulfur dioxide: SO₂ 2. Heavy metals: lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium ion (Cd) 3. Hydrogen chloride: HCl 4. Hydrogen sulfide: H₂S | Thermal power plants, chemical plants, smelters, waste incineration plants |
| Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) | 1. Efficient decontamination: decompose pollutants under ultraviolet light 2. Enhanced catalysis: improve photocatalytic efficiency 3. Extended life: reduce the risk of catalyst deactivation | 1. Organic pollutants: benzene (C₆H₆), formaldehyde (CH₂O), xylene (C₈H₁₀), glyphosate (C₃H₈N₃O₅P), methylene blue (C₁₅H₁₉N₃S) 2. Bacteria and viruses: Escherichia coli and viruses 3. Heavy metals: lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd) 4. Chlorine and ammonia: chlorine (Cl₂) ammonia (NH₃) | Water treatment plants, chemical plants, sewage treatment plants, air purification equipment manufacturing plants, food and beverage processing plants, pharmaceutical plants |
| Zinc Oxide (ZnO) | 1. Catalyst: Promote chemical reactions 2. Enhance adsorption: Improve the adsorption effect of pollutants 3. Antibacterial: Improve the sterilization ability in water treatment and air purification 4. Photoelectric applications: Can be used for photoelectric materials 5. Environmental governance: Effectively remove heavy metals and organic pollutants | 1. Heavy metals: lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg) 2. Organic pollutants: benzene (C₆H₆), toluene (C₇H₈), phenols (C₆H₅OH) 3. Pathogenic microorganisms: bacteria and viruses 4. Ammonia: (NH₃) | Water treatment plants, wastewater treatment plants, chemical plants, air purification equipment manufacturers, pharmaceutical plants, food processing plants |
| Biocatalysts | 1. Accelerate the reaction: increase the rate of chemical reactions 2. Selective catalysis: reduce the generation of by-products 3. Environmental protection: use natural materials to reduce environmental impact 4. Energy saving: react under mild conditions 5. Renewable: can be cleaned and restored to extend service life 6. Enhance adsorption: combine adsorption and catalysis to improve the effect | 1. Organic pollutants: COD, BOD 2. Heavy metals: lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg) 3. Ammonia nitrogen: ammonia (NH₃) 4. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): toluene (C₇H₈), benzene (C₆H₆) 5. Pigments: methylene blue (C16H18N3S) 6. Microorganisms: pathogens and bacteria | Sewage treatment plants, chemical plants, printing and dyeing plants, electroplating plants, pharmaceutical plants, food processing plants |
| Lanthanum La | 1. Remove phosphates: prevent eutrophication of water bodies 2. Adsorb heavy metals 3. Remove fluoride: improve water quality | 1. Phosphate: (PO₄⁻) 2. Heavy metals: lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd) 3. Fluoride ion: F | Sewage treatment plants, drinking water treatment plants, electronics manufacturing plants, chemical plants |
| Cerium | 1. Remove heavy metals: adsorb metal ions in water 2. Oxidative degradation: decompose hard-to-degrade organic pollutants 3. Enhance phosphorus removal: improve the effect of phosphoric acid removal 4. Extend service life: reduce regeneration requirements | 1. Heavy metals: lead ion (Pb), cadmium (Cd) 2. Phosphate: (PO₄3-) 3. Organic pollutants: methyl blue (C₁₈H₁₈N₃S) | Water treatment plants, chemical plants, pharmaceutical plants, electroplating plants, metallurgical plants |
| Reactive Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) | 1. Remove pollutants 2. Catalytic reaction: convert nitrogen oxides into harmless substances 3. Improve performance: improve the selectivity and adsorption capacity of activated carbon 4. Enhance reaction activity: increase the activity of chemical reactions | 1. Nitric oxide (NO) 2. Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) | Thermal power plants, cement plants, chemical plants, steel plants, oil refineries, motor vehicle exhaust treatment plants |
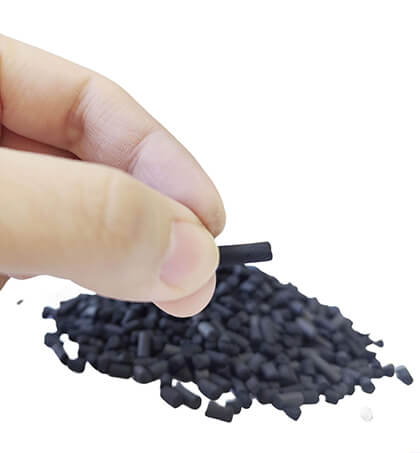

Heycarbons Catalytic Pelletized Activated Carbon
Heycarbons extruded/columnar/pelletized catalytic activated carbon include coal/coconut shell/wood base catalytic pelletized activated carbon .
The supported catalyst comprises: Manganese dioxide (MnO₂), iron oxide (Fe₂O₃), copper oxide (CuO), magnesium oxide (MgO), cobalt oxide (Co₃O₄)
Platinum (Pt), Palladium (Pd), Silver (Ag),CaCO,TiO₂Titanium dioxide (TiO₂), zinc oxide (ZnO),Vanadium (V), Nickel (Ni)…
Reactive Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) Adsorption Materials…
- Size (D: mm): 0.9mm, 1.5mm, 2mm, 3mm, 4mm, 5mm, 6mm, 8mm
- CTC(%): 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 120
- Iodine value: Mg/g 500-1500
- Hardness (%): 95-99
- Moisture (%): ≤3
You will get a quote in 24 hours
Heycarbons Coconut Shell Catalytic Granular Activated Carbon
Heycarbons Coconut shells granular catalytic activated carbon.
This catalytic carbon is not impregnated with caustic chemicals used to remove chloramines and hydrogen sulfide H2S from drinking water.
The video is Coconut shell catalyst granular activated carbon VS ordinary coconut shell gac
The supported catalyst comprises: Manganese dioxide (MnO₂), iron oxide (Fe₂O₃), copper oxide (CuO), magnesium oxide (MgO), cobalt oxide (Co₃O₄)
Platinum (Pt), Palladium (Pd), Silver (Ag),CaCO,TiO₂Titanium dioxide (TiO₂), zinc oxide (ZnO), Vanadium (V), Nickel (Ni)…
Reactive Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) Adsorption Materials…
- Size: Mesh 4*8, 8*30, 8*16, 12*40, 30*60, 80*150
- Iodine value: Mg/g 700-1700
- Hardness %: 90-99
- Moisture %: 5max
You will get a quote in 24 hours
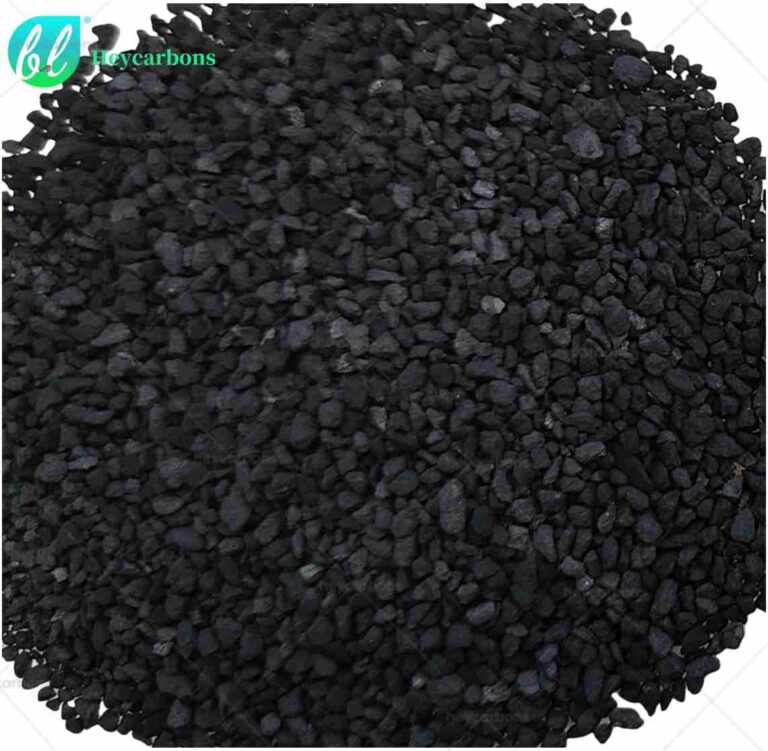

Heycarbons Coal Granular Catalytic Activated Carbon
Heycarbons Coal catalytic granular activated carbon.
There are also coal reagglomerated briquetting catalytic granular activated carbon.
The supported catalyst comprises: Manganese dioxide (MnO₂), iron oxide (Fe₂O₃), copper oxide (CuO), magnesium oxide (MgO), cobalt oxide (Co₃O₄)
Platinum (Pt), Palladium (Pd), Silver (Ag),CaCO,TiO₂Titanium dioxide (TiO₂), Zinc oxide (ZnO),Vanadium (V), Nickel (Ni)…
Reactive Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) Adsorption Materials…
- Size: Mesh 4*8, 8*30, 8*16, 12*40, 30*60, 80*150
- Iodine value: Mg/g 700-1700
- Hardness %: 90-99
- Moisture %: 5max
You will get a quote in 24 hours
Customize Heycarbons Catalytic Activated Carbon Solution
Heycarbons provides a full range of activated carbon solutions at competitive prices.
You will get a quote in 24 hours
Why choose Heycarbons Catalytic Activated Carbon
Heycarbons has proudly served the activated carbon industry with high-quality products since 2005, we can customize your catalytic activated carbon for your project.
- What our customers say about us?
- Customize different raw materials according to different applications.
- Customize the type of added substance or catalysts substance. also customized size, CTC, iodine value, ash, etc.
- Cost-effective solutions customized according to customer applications.
- Heycarbons customized package to promote your brand, and free design service.
Call Us
+86-180 3788 5195
Our Email
info@heycarbons.com
Steps to Custom Heycarbons Catalytic Activated Carbon
Consultation
By understanding your needs and requirements, our salesmen work with you to submit the appropriate activated carbon solution.
Quotation
Heycarbons expert customer service will provide you with a free quote based on your requirements as well as product specifications and quantities.
Production
Heycarbons has sufficient inventory and strong production capacity, and will report production progress to you from time to time.
Shipping
Heycarbons know you need to receive the product as soon as possible, after rigorous quality checks and protective packaging, by fedex shipping.
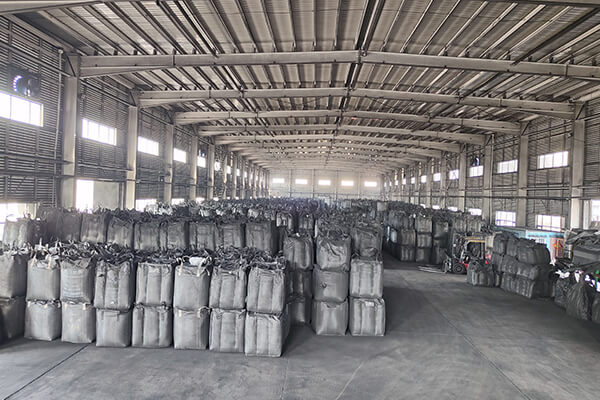
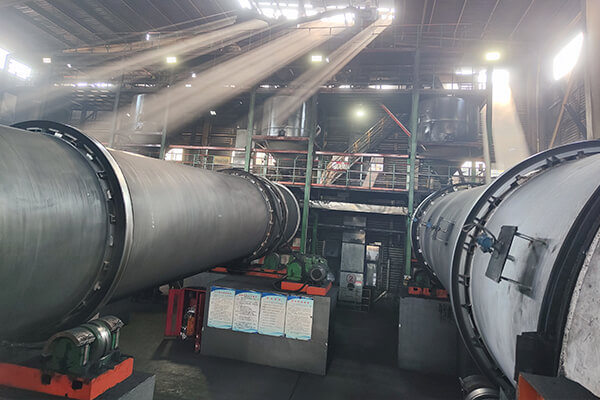












Are You Looking for Heycarbons Catalytic Activated Carbon Manufacturers?
Contact us for design assistance, free quote, and expert advice today.
Your inquiry will be replied within 24 working hours, and Heycarbons respect your privacy.
You will get a quote in 24 hours


